Is this truly your body?
A story on Scoliosis
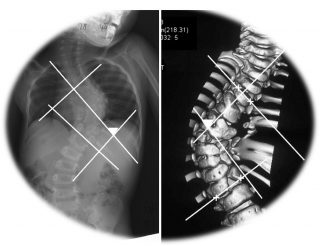
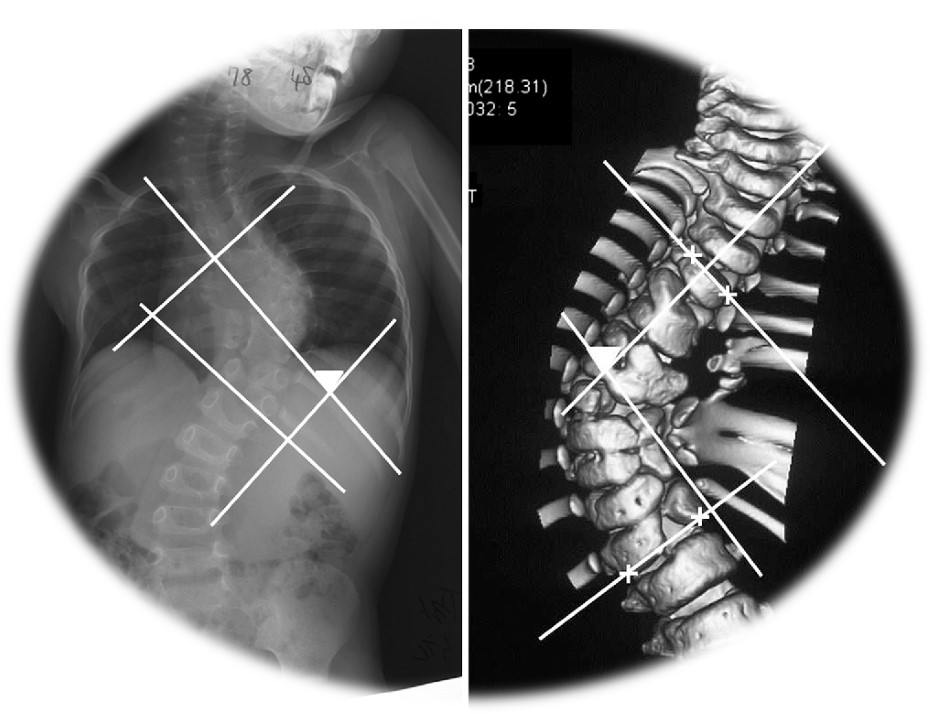
The origin of the vertebrae is derived from the Greek word ‘skolios’, which is used to describe when the vertebrae is curved to the side C-shape or S-shape. When the flexion of the Cobb angle occurs more than 10 degrees, it is called Scoliosis. Most scoliosis progresses slowly from the age of nine and progresses more rapidly during the period of active growth. When a set of growth is over, the possibility of making more curves is lowered, but it is very difficult from a therapeutic point of view, so it is important that early detection and appropriate treatment begin at the right time.

According to the most recent paper (August 1, 2018, advances in pediatrics, pediatric specialists), it is important to distinguish between functional scoliosis and structural scoliosis, It is claimed that three types of spinal deformity, nerve / muscle disease, and idiopathic should be distinguished. However, it is easy to understand that the spinal cord of the innate and idiopathic cervical spine is divided into two categories.
1. Congenital scoliosis
Congenital scoliosis is largely divided into two types (spinal bony defects or neuromuscular reasons), with a rate of 1/1000 appearing mostly in newborns younger than 3 years old and 1% to 4% worldwide. In the newborn period, there is not much change in the body yet, so when you are in the growth phase when bending or bending occurs, you often find that your child suffers from benign scoliosis. Congenital scoliosis is mainly caused by the merging of the wrong vertebrae or defects of the other vertebrae that were born congenitally, and 61% of the neonates with congenital scoliosis are found in the anus, heart disease, Symptoms, and kidneys.
In the case of congenital scoliosis of newborn babies, it is said that a child can find out some information by ultrasound when yet unborn. You can also predict on a newborn baby by a simple check from the external view of the eye to check whether there is a part of skin wrinkled, a part that is slightly caved in at the ends of both vertebrae, pieces of hair on the spine or a red hemangioma.
In the case of congenital scoliosis, neurological examination, sensory integration test, stimulus reflex test, etc. are performed and an x-ray is taken every 3 months to observe the changing process. Children with congenital scoliosis usually have one end of the vertebrae stuck together and lung function and cardiac function may deteriorate, so it is absolutely discouraged to wear orthotics. Observations using x-ray at 3-month intervals, and if the progression rate of scoliosis progresses significantly, many cases are treated with surgery.
2. idiopathic scoliosis Idiopathic scoliosis occurs without any specific reason, and is usually the case with all scoliosis from 75% to 80%. So far, many theories have emerged to explain the reason for scoliosis without a specific cause of the disease. 1. Bio-mechanical dysfunction (functional scoliosis) 2. Neurological dysfunction 3. Hormonal imbalance 4. Environmental factors belong to those theories. These four theories commonly claim that “growth plates are irregularly stimulated wherever there is much stimulation, the rate of growth increases faster, and where less stimulation occurs, the rate of growth slows significantly.”
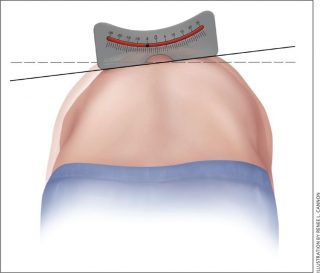
The most commonly reported factor in recent articles is scoliosis caused by a disruption of balance between muscles that come from bio-mechanical dysfunction, i.e. muscles pulling the spine across the vertebrae. Idiopathic scoliosis can be easily checked at home. The most commonly performed tests are the “Adams forward-bending test”, which compares the height of either ribs or scapulae by bending the waist forward and finding the most basic information.

If the difference between both sides exceeds 7 degrees, it is better to check with Cobb angle on X-ray. Most idiopathic scoliosis occurs in 45% of patients with scoliosis, and 40% of patients have scoliosis in the lumbar spine.
These idiopathic scoliosis are divided into progressive scoliosis and non-progressive scoliosis. When the Cobb angle exceeds 20 degrees by X-ray, it is usually referred to as phase 2 idiopathic scoliosis. The growth of the pelvis is measured by the pelvic x-rays. It is important to calculate how much growth is left and treat this. If idiopathic scoliosis is non-progressive scoliosis with a Cobb angle of less than 20 degrees, it is easy to overcome with basic exercise and stretching.

Treatment for idiopathic scoliosis is usually aimed at no longer having more flexion. However, in the case of idiopathic scoliosis of 10%, exercise therapy or treatment should be performed concurrently to prevent future backache, chest pain, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. Therefore, whether or not treatment should be included, what kinds of exercises, and whether the stretching should be a precise diagnosis should be the top priority. Scoliosis is not a condition that can be overcome as a day or week of effort and treatment by taking medication. You can see the effect only when you are willing to build a brick towards recovery every day. Have a look at the mirror while you are reading this. This is the posture of your usual self that the body did not know itself had. It is the first step to overcome all conditions; to recognize your own condition yourself.